India’s Booming Automobile Market and MSME Sector
India Ranks as the World’s Third-Largest Automobile Market
India ranks as the world’s third-largest automobile market, contributing 7.1% to the country’s GDP and providing employment to 37 million people. Additionally, the industry holds a 4.7% share in India’s exports and accounts for 40% of global R&D. Notably, India plays a significant role in the global heavy vehicle market, as the largest tractor manufacturer, the second-largest bus manufacturer and the third-largest heavy truck manufacturer worldwide. The Indian automotive market has witnessed significant growth, reaching a value of USD 116.86 billion in 2023, reflecting an 8.10% growth from USD 108.10 billion in 2022.
Government Initiatives Driving Growth in the Automobile Industry
Government initiatives such as the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme have been particularly successful, attracting a proposed investment of ` 67,690 crore, surpassing the initial target estimate of ` 42,500 crore over a five-year period. Additionally, proactive measures such as ‘Make in India’, the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) and schemes like the Advance Authorisation and Export Promotion Capital Goods Scheme have been implemented, boosting manufacturing and automobile exports.
Technological Advancements Boost Digital Adoption
Digital adoption and technological upgradation have emerged as key driving factors, with the adoption of connected automotive technology witnessing a rise in India. This facilitates integrating vehicles with internet connectivity, enabling features such as real-time navigation, remote diagnostics and vehicle-to-vehicle interaction.
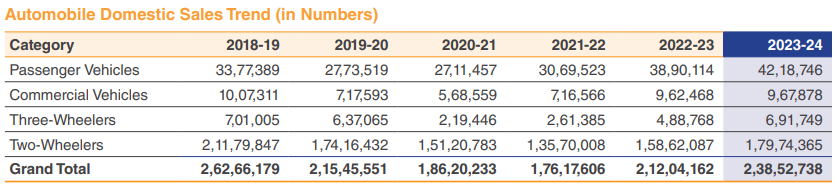
Surge in Domestic Automobile Sales
During FY 2023-24, total domestic automobile sales surged to 23.85 million units, compared to 21.20 million units during the last financial year. The Passenger Vehicles (PV) and the three-wheelers segments experienced strong volume growth, with increases of 8.45% and 41.53%, respectively, during the fiscal year. PV sales reached 42,18,746 units, and CV sales reached 9,67,878 units. This growth was propelled by factors such as the expanding middle class, increasing disposable incomes, evolving consumer preferences, and enhanced infrastructure availability in India.
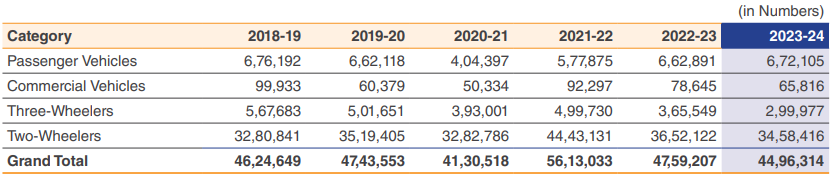
Indian Automobile Export Trends
India is a significant player in the global automobile export market, yet it experienced a 5.5% decline in automobile shipments during FY 2023-24. The overall export during the financial year stands at 45,00,492 units compared to 47,61,299 units in the last financial year. This decline was primarily driven by overseas markets grappling with monetary and geopolitical crises. The Passenger Vehicle (PV) segment was the sole segment to showcase growth, with shipments increasing by 1.4% to reach 6,72,105 units. This growth in the PV segment can be attributed to Indian regulatory norms aligning with global standards, resulting in vehicles being developed and sold with minimal adaptation required for export markets.
On the other hand, the government is supporting the automobile industry through initiatives such as the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) and Make in India, which aim to enhance manufacturing capacity and stimulate exports. Additionally, the industry’s ongoing innovation and development of advanced technologies suggest the potential for further growth in exports.
Positive Outlook for the Indian Automobile Industry
The Indian automobile industry is poised for significant growth, projected to increase from USD 116.86 billion in 2023 to USD 217.90 billion by 2031, indicating a CAGR of 8.1%. This growth will be driven by several factors, including increasing domestic demand and favourable government policies. Additionally, the industry’s ability to adapt to future trends such as the rising demand for electric vehicles. Government support through policies and initiatives like Automotive Mission Plan 2026, and scrappage policy will also play a crucial role in driving this growth.
The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) Sector
India is the world’s second-largest MSME base after China. Indian MSMEs contribute approximately 30% to the country’s GDP, 6.11% to manufacturing output, and 25.63% to the services GDP of the Indian economy. The sector offers a diverse range of services and manufactures over 6,000 products, ranging from traditional to high-tech items.
MSME Sector Witnesses Significant Expansion
The MSME sector witnessed significant expansion during 2023 with Udyam registrations surging from 1.31 crore as of December 31, 2022, to a total of 2.19 crore. 88.89 lakh registrations were recorded between January and December 2023. Additionally, a collaborative effort between the Ministry and Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) led to the launch of a portal, for integrating Informal Micro Enterprises (IMEs) into the formal sector. Approximately, 1.11 crore IMEs have been onboarded onto the UAP through this initiative. These initiatives have facilitated sectoral growth during the financial year.
Government Support Enhances MSME Sector Growth
During the year of reporting, the growth of MSMEs was supported by the proactive assistance of the Indian government. The government focussed on aiding the growth and progress of MSMEs, implementing various measures to tackle their specific challenges and promote their expansion. During the 2023-24 budget, the government announced the PM Vishwakarma initiative, allocating ` 13,000 crore for an initial five-year period. As of December 30, 2023, a total of 48.80 lakh enrolments have been recorded under PM Vishwakarma. Also, the government undertakings will refund performance security which was deducted during the COVID-19 pandemic under the Vivad se Vishwas – I. The Credit Guarantee for Micro and Small Enterprises(CGTMSE) was revamped in the year 2023 where the ceiling limit of Guarantee coverage was increased from ` 2 crore to ` 5 crore.
Government Initiatives Empowering MSMEs
Apart from financial assistance, the government has also launched programmes like Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) and the MSME Self-Reliant India Fund (Fund of Funds) to empower MSMEs through technology upgrades, skill development, and access to markets. Through these initiatives, the government aims to cultivate a more inclusive financial ecosystem. This approach can help India unlock the full potential of its MSME sector, thereby fuelling additional economic growth and job creation.
Addressing Financing Challenges in the MSME Sector
Despite the sector being the country’s socio-economic development, securing adequate financing poses a key challenge for MSMEs. An estimated credit gap of ` 33 trillion obstructs the growth potential of these enterprises also the MSMEs were facing the challenge of the working capital gap. As per the IFC report, formal credit channels, address only a fraction of this need, providing just ` 10.9 trillion
This leaves a substantial financing gap of ` 22.1 trillion with 67% of this demand attributed to fulfilling working capital needs. To overcome the challenges, MSME working capital loans help the industry. Also, the development of standardised and easily accessible working capital products can offer MSMEs the financial flexibility required for their growth and success.
Positive Outlook for the MSME Sector
The Indian economy is poised to achieve the milestone of a USD 5 trillion economy by 2027-28, with MSMEs expected to be a driving force behind this growth. This sector stands as a crucial pillar of the Indian economy, making substantial contributions to its growth, employment, and exports. Economists project that by 2028, the MSME sector will be valued at ` 1 trillion, with 63.4 million MSMEs making significant contributions to the Indian economy. This growth will be driven by the digitalisation of the sector, Skill Training Eco-system of the Ministry of MSME and the recent support shown by the government. MSMEs are wellpositioned to drive widespread economic growth, create employment opportunities, and foster entrepreneurship across the nation
Loan Against Property
In India, Loan Against Property (LAP) is a financial product frequently provided by NBFCs to SMEs. LAP is a type of loan secured against property. It offers benefits like no end-use restrictions, income tax exemptions, competitive interest rates, affordable EMIs, digital monitoring, long repayment duration, and income tax exemptions. The demand is also driven by lower interest rates, quick approvals, and flexible terms. In recent years, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) have shifted their focus from medium ticket loans to the Small Ticket Loan Against Property (S-LAP) segment. The estimated market potential for S-LAP stands at ` 22 lakh crore. However, as of March 2023, lenders have only tapped around ` 1.8 lakh crore, indicating a penetration rate of less than 10%, according to ICICI Securities report.
NBFC Sector Overview
In recent times, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) have emerged as significant players in India’s financial Industry, catering to the changing credit needs of the commercial sector. As of 2023, the size of the NBFC sector is estimated to be around USD 326 billion. The sector’s remarkable growth is driven by various factors, such as a rising middle class, enhanced financial inclusion and positive policy interventions. Initiatives from the government and central banks like Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY), and Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) have supported the growth of the industry.
Dominance of Housing and Infrastructure Loans
In terms of asset size-wise mix, housing loans and infrastructure loans remain predominant within the overall NBFC portfolio. Microfinance loans have seen a marginal improvement in their share, from approximately 2% to 3% between FY 2019-28 and FY 2022-23. It is expected that housing and infrastructure loans will maintain their share in the overall NBFC credit ecosystem.
Substantial Credit Growth in the NBFC Sector
Between September 2022 and September 2023, the NBFC sector in India experienced substantial credit growth, with gross advances rising by 20.8% year-on-year up from 10.8% in the previous year. As per RBI data, the credit quality of the NBFCs has been improving on account of strong domestic demand, improving credit conditions for bank borrowers, and strengthened solvency and funding of Indian financial institutions. The report states that the Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio for government NBFCs has reduced to approximately 2.5%, while for private NBFCs, it stands at about 6.1%. The Net Non-Performing Assets (NNPA) ratio has also improved, supported by a healthy Provision Coverage Ratio (PCR).
Diversification of Funding Sources by NBFCs
n recent years, NBFC have diversified their funding sources beyond traditional funding sources such as banks and debentures. They are now exploring private equity, venture capital, securitisation, and collaborating with ARCs to manage risk and optimise balance sheets.
Positive Outlook for the NBFC Sector
With notable improvement in asset quality and stronger balance sheets observed in 2023, research estimates that NBFC credit is poised to increase at a CAGR of 13–15% between FY 2022-23 and FY 2024-25. This growth trajectory is attributed to the evolving needs of the customer, solid risk management, and the growing demand for seamless and instant services through digital technology. To capitalise on these trends, NBFCs are expected to leverage strategic collaborations, embrace technological advancements, and prioritise financial inclusivity. Government initiatives, coupled with the ongoing digital transformation, are creating a conducive environment for NBFCs to expand credit access to unbanked and underserved segments.