
Technology for Financial Inclusion in India
India’s Fintech sector is expected to contribute a massive $400 to the national economy in the coming years. Today, technology is affecting every aspect of our lives, and it has become very important to use its power to foster financial inclusion.
This factor becomes more prominent in countries like India, where millions of people are still underserved by traditional banking systems.
In the blog, we are going to explore how technology is driving financial inclusion in India and the various advancements behind this positive change.
As per RBI’s (Reserve Bank of India) annual Financial Inclusion Index (FI- Index) improved by 10.5 percent from 2017 to 2021, stating that financial inclusion is deepening in rural India. Under PMJDY, 44.63 crore accounts were opened with deposits of more than 1.5 lakh crore in these accounts in last 7 years.
Let’s start by understanding what exactly financial inclusion is!
What is Financial Inclusion?
Financial Inclusion or inclusive finance refers to the efforts to provide affordable and appropriate financial services such as,
- Transactions,
- Payments,
- Savings,
- Credit and insurance
to all people and businesses, despite of their income and company size.
The main goal of inclusive finance is to ensure that financial services are accessible to all sections of society, especially marginalized or underserved.
Further, People also need to actively use financial services to derive benefit from them. Moreover, services should be of high quality, with transparency, easy understandability, and should offer fair terms and conditions. For instance, quality banking services should have reasonable fees, clear terms for loans, and reliable customer support.
Importance of Financial Inclusion For Marginalized and Underserved Populations
1) Reduces poverty and inequality
Inclusive finance helps reduce poverty for marginalized and low-income individuals. It provides increased opportunities and access to formal financial services, like savings, credit, and insurance.
This, in turn, helps manage finances, and individuals can invest in income-generating activities. Ultimately, they can lift themselves out of poverty and create new opportunities for economic stability.
2) Promotes economic growth
Increased access to financial services will have a direct impact on our economy. Credit will help entrepreneurs start their businesses, families invest in education and housing, and communities build infrastructure.
3) Empowerment
Previously, women were not given freedom in marginalized communities. But financial inclusion is all about empowering everyone, including those who’ve been left out before.
Imagine a woman being able to open a bank account or get a loan. This would give her more control over her money, which she could use to invest in her children’s education or secure better healthcare for the family.
4) Social Inclusion
Financial inclusion often goes hand in hand with social inclusion. It’s all about ensuring that everyone has an equal chance to participate in society. Unfortunately, when people don’t have access to basic financial services, it can make them feel left out and disconnected from the rest of society.
But when financial services are expanded to these underserved populations, people feel more confident and connected to their communities.
5) Promotes innovation
It promotes innovation by creating a demand for new solutions that cater to the needs of underserved populations. When more people, especially those previously excluded from traditional banking, gain access to financial services, it prompts financial institutions to develop innovative technologies and strategies to serve this growing market.
Moreover, the development of these new technologies benefits more than just the underserved. It often leads to improvements in financial services for everyone, making processes more efficient, cost-effective, and convenient.
6) Supports small businesses
Financial inclusion boosts small businesses by offering them better access to funding. Traditional banks can sometimes be tough for small businesses to get loans from. But with financial inclusion, new ways of lending are emerging, like peer-to-peer lending platforms or microfinance institutions.
In a nutshell, it opens up opportunities for small businesses to thrive and grow.
Now, let’s have a look How is Technology Driving Financial Inclusion In India?
According to a report by Global Findex, 76% of the global population has an account (a/c) with a financial institution or a mobile money provider. On the other hand, 80% of Indian adults possess a bank account.
Despite such large numbers, challenges remain, especially for MSMEs, which play an important role in contributing to India’s GDP.
These challenges include,
- Limited access to credit,
- Complex application processes and
- Strict collateral requirements.
Technology for financial inclusion is solving all these problems. Here’s how!
- AI and machine learning algorithms make precise credit risk assessments by analyzing alternative data sources. This helps individuals to get credit access without established banking histories.
- Emerging financial models such as Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) allow consumers to make purchases without paying for them all at once. Instead, they can pay over time without incurring extra charges, which is particularly helpful for individuals who may struggle to afford purchases upfront.
- For MSMEs, the Faster Rotation Credit Line (FRCL) model is proving to be transformative. It functions similarly to a credit card for small businesses but is easier to obtain and can be used multiple times within a specified credit term.
- Another significant development is the concept of open banking, which uses Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). It allows users to securely share their banking information with different companies, enabling them to access various financial services from different providers through their bank accounts.
Challenges of Financial Inclusion in India:
Some of the major challenges hindering technology for financial inclusion in India include:
1) Non-price barriers
Proper document proof, including a person’s identity, address, income, etc., is required to use financial sources. Generally, people in the underserved category do not have these documents, and as a result, they are not given the benefit of these services.
2) Behavioral aspects
According to the IDBI Gilts Report, a significant portion of the population is not comfortable using formal financial services. Why? Because they find it difficult to understand the language and related terms. The individuals also think that these services are only meant for the upper strata of society.
3) High cost for service provider & utiliser
Providing and utilizing financial services is not as easy as it seems. Of course, it comes with a cost for both the service provider and the utiliser. Here’s how!
- Cost for the service utiliser: The procedure of setting up new branches in rural areas comes with high-cost and low business.
- Cost for the service provider: People living in marginalized communities show hesitation in using these services due to
high costs, minimum account balance requirements, loan processing charges, etc.
4) Financial illiteracy
People who want to use financial services must have at least limited financial knowledge, such as basic mathematics and English. However, the ones living in small villages do not have that much of an understanding either, which becomes a major constraint while accessing financial services.
5) Technological hindrances
Some people feel nervous or unsure about using new technology for their banking needs. They might worry about security or simply feel uncomfortable with the unfamiliarity of digital banking platforms.
6) Social barrier
This factor comprises two major issues:
- Gender concerns: This problem mainly arises in the case of women as they face difficulties getting loans because they might not own property or land. Sometimes, they need a man to guarantee their loans, which can make it even harder for them to borrow money.
- Age issues: Banks usually focus on serving the economically active population, and they often overlook the financial needs of younger and older demographics.
Fintech Solutions for Financial Inclusion in India | Technology for Financial Inclusion
Fintech companies are playing a very important role in promoting financial inclusion in India.
They are reaching marginalized and underserved populations to provide access to financial services, like banking, credit, and insurance.
According to a report by BCG, India’s fintech market is forecasted to reach $200 billion in revenue by 2030.
Now, let’s have a look at some of the fintech solutions that are promoting inclusive finance.
1) Digital Payments
Digital or electronic payments do not involve a physical transfer of currency. They eliminate the need for cash management and provide a clear trail for accounting purposes. These payments are made using digital payment platforms.
The different digital payment methods available in India are:
- Banking Cards
- Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AEPS)
- Unstructured Supplementary Service Data(USSD)
- Mobile Wallets (According to a report by Mastercard, 76% of customers believe that mobile wallets offer a more convenient payment method than traditional options.)
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
- PoS Terminals
- Mobile Banking
- Internet Banking
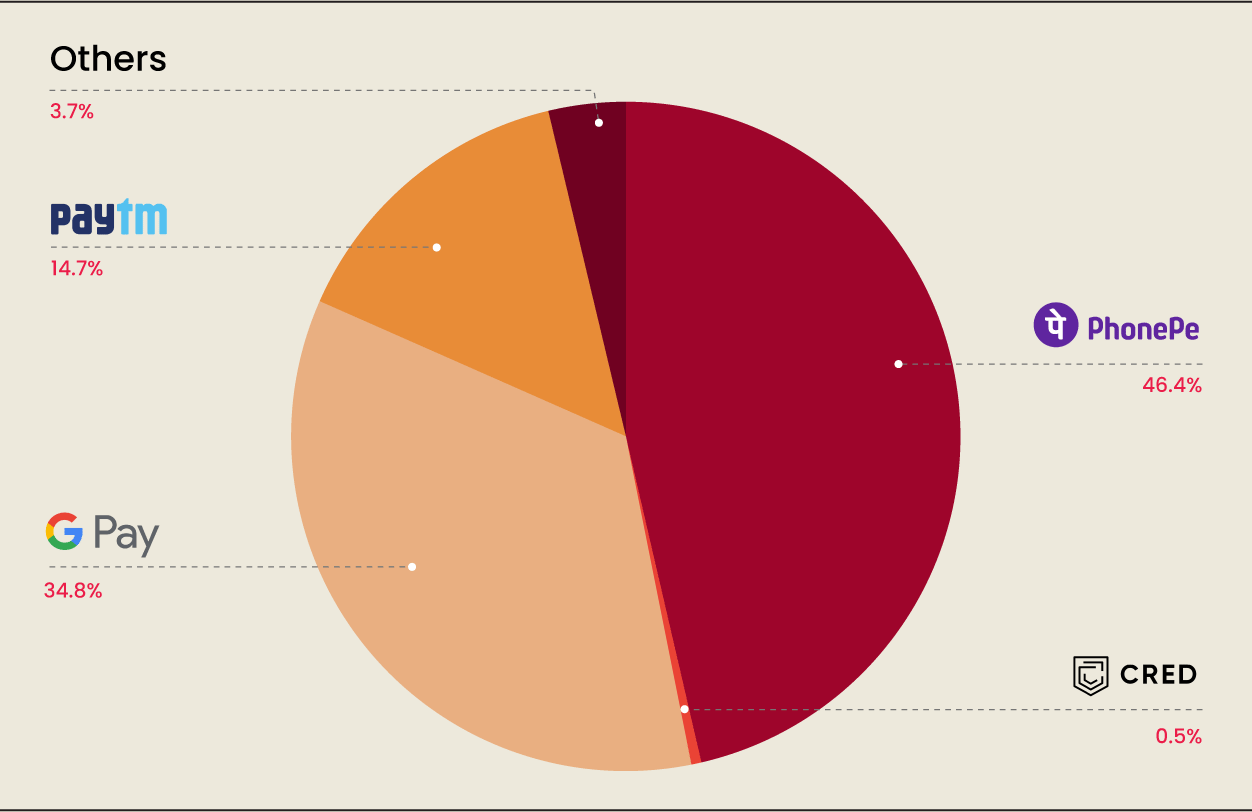
With technological advancements, India is seeing several successful fintech startups that are promoting technology for financial inclusion. Some of the popular names among them are Google Pay, Paytm, CRED, PhonePe, and others.
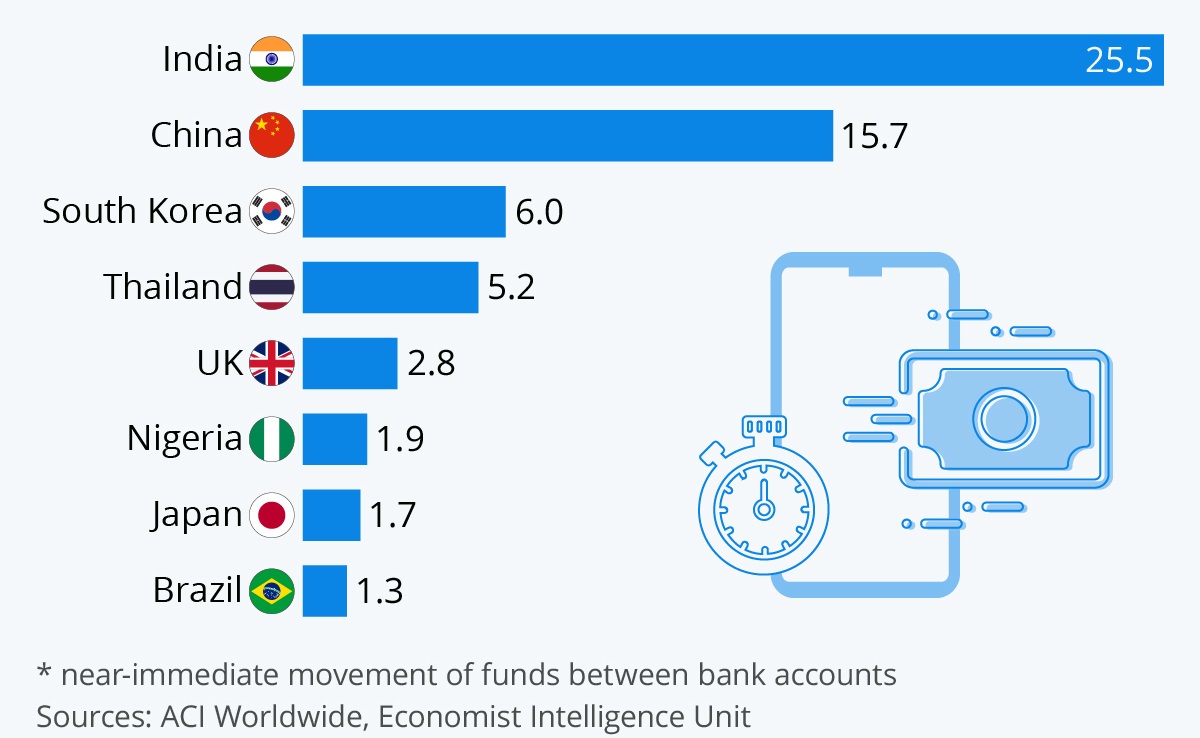
Countries with the highest number of Real-time payment systems
2) Microfinance Platforms
Fintech platforms have facilitated the delivery of microfinance services to underserved populations, including small-scale entrepreneurs and low-income individuals. These platforms use digital lending algorithms and alternative credit scoring methods to extend small loans to borrowers who may not have access to formal banking channels.
Some of the key benefits of microfinance include:
- Provides easy access to credit which other banks don’t usually offer.
- Allows people to explore new possibilities and makes future investment possible.
- The best part about these loans is that they are mostly taken by women.
- Results in better credit management practices.
- Caters for the under-financed section of society, including unemployed people and those with disabilities.
3) peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms:
P2P lending platforms connect borrowers directly with lenders through online marketplaces, bypassing traditional financial intermediaries. These platforms provide affordable credit options to individuals and small businesses that may be excluded from the formal banking sector due to lack of collateral or credit history.
The key benefits of P2P include:
- P2P lending platforms provide fast services with minimal documentation and eliminate lengthy documentation.
- The loan approval process is much faster.
- The lenders are allowed to invest in multiple loans with different risk ratings. This helps them to diversify their portfolio, minimizing risks and maximizing returns.
- People can also invest in these platforms to get a high Return on Investment (ROI).
4) Insurtech Solutions
Insurtech solutions are technological innovations and applications that aim to enhance and revolutionize the insurance industry. These solutions leverage advancements in technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, big data analytics, Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and mobile technology to streamline processes, improve customer experience, and mitigate risks. Insurtech solutions encompass a wide range of applications, including digital insurance platforms, usage-based insurance, telematics for risk assessment, automated claims processing, chatbots for customer service, predictive analytics for underwriting, and blockchain for secure data management and smart contracts. By integrating these technologies, insurtech solutions enable insurance companies to operate more efficiently, offer personalized products and services, and adapt to changing market dynamics, ultimately driving innovation and competitiveness in the insurance industry.
6) Alternative Credit Scoring:
Fintech firms leverage alternative data sources, such as mobile phone usage, utility bill payments, and social media activity, to assess creditworthiness and extend credit to individuals who lack traditional credit histories. By using innovative credit scoring models, fintech companies enable underserved populations to access loans and other financial products.
Government initiatives promoting digital financial services through technology:
1) Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
This scheme aims to take financial literacy up to the village level and provides a platform for universal access to banking facilities, including
- Financial literacy,
- At least one basic banking account for every household,
- Access to credit, insurance and pension facilities.
2) Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyaan (PMGDISHA)
- This scheme focuses on promoting digital literacy in rural areas. It aims to empower at least one person per household with the knowledge and skills required to access digital financial services.
- By providing the necessary training, PMGDISHA encourages the adoption of cashless transactions and online banking.
3) Digital India
It encompasses key vision areas of:
- Digital empowerment of citizens.
- Governance and services on-demand.
- Digital infrastructure as a core advantage to every Indian citizen.
4) Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS)
- Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS) is a bank-led model. It allows interoperable financial inclusion transactions at PoS or Point of Sale (MicroATM) through the business contributor of any bank using the Aadhaar authentication.
- Some of the banking services offered by AePS,
- Cash Withdrawal
- Balance Enquiry
- Cash Deposit
- Authentication
- BHIM Aadhaar Pay
- Aadhaar to Aadhaar Fund Transfer
- Mini Statement
5) Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
Unified Payments Interface or UPI is a real-time payment system that powers:
- Multiple bank accounts (a/c) into a single mobile app,
- Merges different banking features,
- Seamless or impeccable fund routing & merchant payments into one hood.
- Inadequate infrastructure and non-accessibility of appropriate financial products, especially in rural areas.
- Low financial literacy
- As finance heavily relies on data, ensuring the privacy and security of individuals’ data is vital.
- Improper internet connectivity results in significant barriers to fintech adoption.
- Lack of trust in banking institutions, and so on.
Impact of Tech-Driven Financial Inclusion in India | Technology For Financial Inclusion
Technology has played a major role in the realm of financial inclusion. Tech-driven initiatives in India have brought significant positive impacts across various aspects of society and the economy. Below are some!
1) Empowerment of Marginalized Communities
By using technology, more people, including those who live in rural areas or have low incomes, can now access banking services. This means they can save money, get loans, and use other financial services that they couldn’t before.
2) Encouraging New Ideas and Businesses
Technology has also helped to create new businesses and generate new ideas. For example, there are now apps that help people manage their money better or get loans more easily.
3) Reduction of Economic Inequality
Tech-driven financial inclusion has also helped to reduce the gap between rich and poor people. Now, even those with lower incomes have a chance to save money, start businesses, and improve their lives.
4) Enhanced Financial Stability
Technology helps individuals mitigate financial risks. Access to savings accounts, insurance, and other financial products enables people to better manage unforeseen expenses.
5) Helping the Economy Grow
When more people use banking services, it helps the whole economy grow. People can invest in businesses, buy things, and create jobs, which makes the country’s economy stronger.
The way forward for Financial Inclusion:
The way forward for technology in advancing financial inclusion involves a concerted effort from various stakeholders to leverage innovative solutions, foster collaboration, and address remaining challenges. Here’s a comprehensive guideline for way forward:
- Innovative Product Development: Fintech companies and traditional financial institutions should continue to innovate and develop products tailored to the needs of underserved populations. This includes expanding digital banking services, offering low-cost payment solutions, and designing accessible credit and savings products.
- Tech driven credit scoring: Embrace alternative data sources and advanced analytics to develop more inclusive credit scoring models. By leveraging nontraditional data such as mobile phone usage, utility bill payments, and social media activity, fintech firms can extend credit to individual with limited or no credit history.
- Infrastructure Development: Improve digital infrastructure, including internet connectivity and mobile network coverage, especially in rural and remote areas. Enhanced infrastructure will enable wider adoption of digital financial services and reduce barriers to access for underserved populations
- Forge Partnerships and Collaborations: Collaboration of Fintech firms with various banks, microfinance institutions (MFIs), government agencies, NGOs, and other stakeholders to maximize their impact on financial inclusion. Partnerships can facilitate knowledge sharing, resource pooling, and the co-creation of innovative solutions that address systemic barriers to financial access and promote sustainable development.
- Promote Financial Literacy and Education: Investment in financial literacy programs, educational content, and interactive tools to empower individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to make informed financial decisions. Promotion of financial literacy and education, can empower users to manage their finances effectively, avoid predatory practices, and build a brighter financial future.
- Drive regulatory innovation and policy support: Engagement with regulators and policymakers to advocate for regulatory frameworks that support innovation, consumer protection, and financial inclusion. By fostering an enabling regulatory environment, policymakers can encourage fintech innovation, mitigate risks, and ensure that financial services are accessible and inclusive for all.
- Addressing Trust and Security Concern: Build trust and confidence in digital financial services by implementing robust security measures, data protection protocols, and fraud prevention mechanisms. Transparency, accountability, and consumer rights should be prioritized to mitigate risks and safeguard user interests.
By embracing these strategies and working collaboratively towards common goals, the way forward for technology in financial inclusion holds the promise of creating a more inclusive, resilient, and equitable financial ecosystem for all.
Conclusion:
Looking towards all the aspects, India will soon become a global pioneer in digital financial services! From making payments online to accessing banking services from far-off places, technology for financial inclusion has changed finance for the better. It’s given many people, who were left out before, a chance to be a part of the financial system.






 Source
Source 







